Freedom
Before the main downloadable text of this post (see below), which is Christopher Caudwell’s essay on “Liberty”, here are two quotations each, first from the philosopher Helena Sheehan, taken from Helena Sheehan’s Christopher Caudwell web page, and then Sheehan's selected quotation from Caudwell (in italics).
The act of knowing transformed what was known. It was never possible to detach the thing known from the knowing of it. Caudwell opposed all passivist imagery in describing knowledge. Knowledge was not a matter of copying, mirroring, photographing, reflecting. Although he never remarked on Lenin's use of such imagery in [Lenin’s] Materialism and Empirio-Criticism, he had read the book and his rejection of the reflectionist model was quite explicit and polemically expressed. In no uncertain terms, Caudwell made his point:
“The mirror reflects accurately: it does not know. Each particle in the universe reflects the rest of the universe, but knowledge is only given to human beings as a result of an active and social relation to the rest of reality.”
In terms of the debate within [Lenin’s] Materialism and Empirio-Criticism, [Caudwell’s] was neither the position of Lenin nor that of Bogdanov. Nor was it the position of Lukacs or Korsch either. It was perhaps the position Gramsci was groping for, but never expressed with such confident clarity as Caudwell. When it came down to it, being preceded knowing, knowing flowed from being and evolved as an extension of being. Decidedly post-Cartesian, Caudwell asserted: I live therefore I think I am. In a concise statement of the fundamental contours of his theory of knowledge, he wrote:
“The question of which is first, mind or matter, is not therefore a question of which is first, subject or object ... Going back in the universe along the dialectic of qualities, we reach by inference a state where no human or animal bodies existed and therefore no minds. It is not strictly accurate to say that therefore the object is prior to the subject any more than it is correct to say the opposite. Object and subject as exhibited by the mind relation, come into being simultaneously.... We can say that relations seen by us between qualities in our environment (the arrangement of the cosmos, energy, mass, all the entities of physics) existed before the subject-object relationship implied in mind. We prove this by the transformations which take place independent of our desires. In this sense, nature is prior to mind and this is the vital sense for science. These qualities produced, as cause and around produce effect, the synthesis, or particular subject-object relationship which we call knowing. Nature therefore produced mind. But the nature which produced mind was not nature "as seen by us." . . . It is nature.... as having indirect not direct relations with us.... Such a view reconciles the endless dualism of mentalism and objectivism. It is the universe of dialectical materialism. Unlike previous philosophies, it includes all reality: it includes not only the world of physics, but it includes smells, tastes, colors, the touch of a loved hand, hopes, desires, beauties, death and life, truth and error.”
Christopher Caudwell’s “Studies in a Dying Culture” were published at a particular moment in history. Caudwell had been killed while defending the Republic in the Spanish Civil War [Image below: Caudwell on the eve of his departure for Spain, from a group photograph]. With its references to his contemporaries H G Wells, Bertrand Russell, and E M Forster (and the 18th-century philosopher Jean-Jaques Rousseau) Caudwell’s essay may seem dated at first glance, but actually, like a lot of Caudwell’s work, it remains critical today and right up to date, in a time when the question of the free-willing human Subject is once again at the forefront.
“Implicit in the conception of thinkers like Russell and Forster, that all social relations are restraints on spontaneous liberty, is the assumption that the animal is the only completely free creature. No one constrains the solitary carnivore to do anything. This is of course an ancient fallacy. Rousseau is the famous exponent. Man is born free but is everywhere in chains. Always in the bourgeois mind is this legend of the golden age, of a perfectly good man corrupted by institutions. Unfortunately not only is man not good without institutions, he is not evil either. He is no man at all; he is neither good nor evil; he is an unconscious brute.
“Russell's idea of liberty is the unphilosophical idea of bestiality… The man alone, unconstrained, answerable only to his instincts, is Russell's free man. Thus all man's painful progress from the beasts is held to be useless. All men's work and sweat and revolutions have been away from freedom. If this is true, and if a man believes, as most of us do, as Russell does, that freedom is the essential goal of human effort, then civilisation should be abandoned and we should return to the woods. I am a Communist because I believe in freedom. I criticise Russell, and Wells, and Forster, because I believe they are the champions of unfreedom.”
Caudwell had got to the heart of the matter: “I am a Communist because I believe in freedom,” he wrote. And what is that? Of all politicians, only those who are communists will be able to answer the question “What is freedom?” in a satisfactory way. Others will echo the sophisticated Bertrand Russell’s bourgeois-romantic version of freedom, as a return to the condition of the wild beasts, or otherwise they will say little, or nothing.
“Power to the People” is our slogan. This is the essence of our project. It means that the masses will have agency. The masses will be human, which is to say, able to think and to act upon their thoughts. This is the active freedom that Caudwell writes about. “This good, liberty, contains all good,” he says.
After Caudwell, and after the war that ended in victory over the fascists against whom Caudwell had fought with his body as well as his pen, bourgeois thinkers did not embrace Caudwell’s idea of liberty. Instead, they fled to irrational, anti-humanist and even outright anti-human philosophies: existentialism, positivism, structuralism, and especially the overtly irrational “Post-modernism” that became the house philosophy of Imperialism. Some of them declared “The Death of the Subject”. In other words, they denied human free will.
In 2002 another English author and philosopher called James Heartfield defied the Post-Modernists and published a book called “The ‘Death of the Subject’ Explained” thereby helping to inspire the Johannesburg Communist University that started in 2003. Heartfield kindly allowed the CU to use extracts from his book. Some of these are contained in the second linked document below.
We communists are for freedom. We are human, not post-human. We are part of a liberation movement, not only of the colonially oppressed, but of humanity worldwide against Imperialism. We are the ones with the theory of freedom. It is the source of our morality. Power to the People! Amaaaaaaaaaandla!
The concept of the free-willing human Subject is the most valuable product of philosophy, including the philosophy of Karl Marx and Frederick Engels. We are going to defend it, including, if necessary, against the concept of materialism, if materialism is taken to say that human life and culture is only a transitory arrangement of molecules.
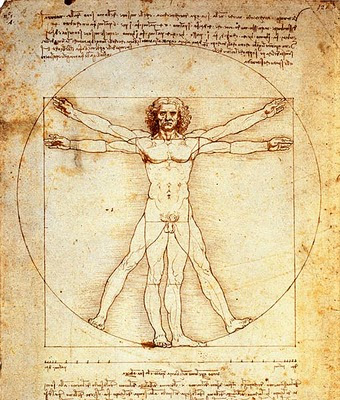
The image at the top of this post is the “Uomo Vitruviano” of Leonardo da Vinci, from the humanist period of the Italian Renaissance. Its meaning is that Man (humanity) is the measure of the Universe.
Please click on the link, download the document and read it, comrades.
Download:
Further reading:
Previous main Communist University posts: | |||
Channel [members] | Course Archive | Weeks | Posted |
SADTU Pol Ed [436] | 6/6 | ||
CU Africa [233] | 6/33 | ||
CU [2924] | 4/10 | ||
Courses completed in 2010 to date: | |||
12 | March - June | ||
10 | January - March | ||
3 days | 2-4 June | ||
10 | March - June | ||
10 | January – March | ||
Click here to visit Marxists Internet Archive | |||



0 comments:
Post a Comment
Post a Comment